Outdated SEO Tactics To Stay Away From in 2018
“There Is Nothing In This World To Fear, But Change.”
WRONG!
Change is necessary. Change is beneficial.
CHANGE IS THE FUTURE.
Why do we say all this? We live in a world that undergoes drastic transitions with each ticking second.
In business, you need to stay updated and in line with the latest trends. To stay on top, you need to embrace change ahead of your competition. We know, to stay on top you need to stay updated. Why?
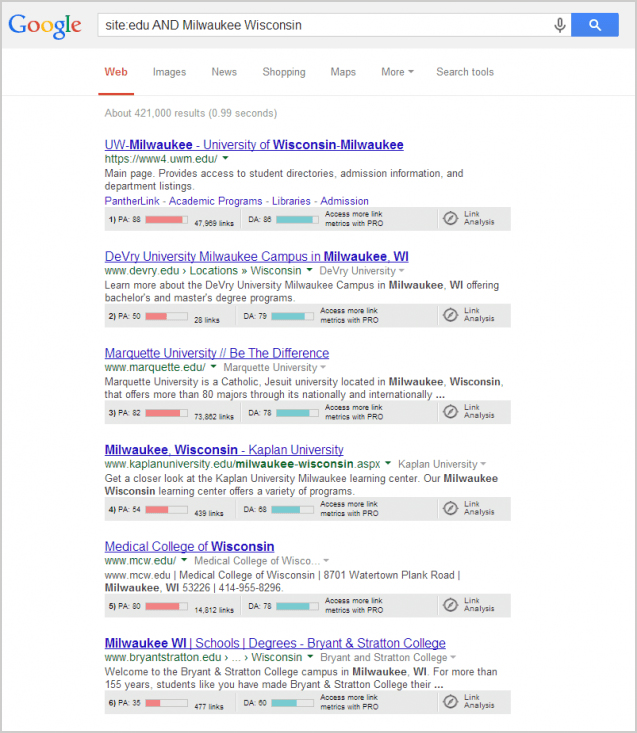
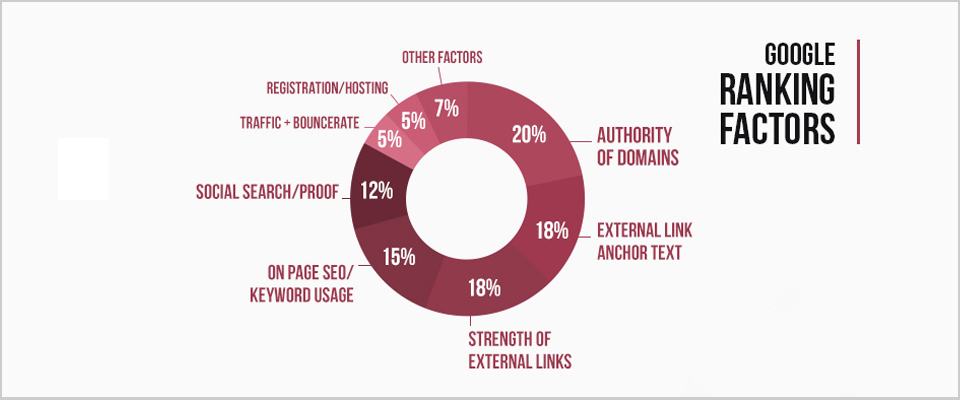
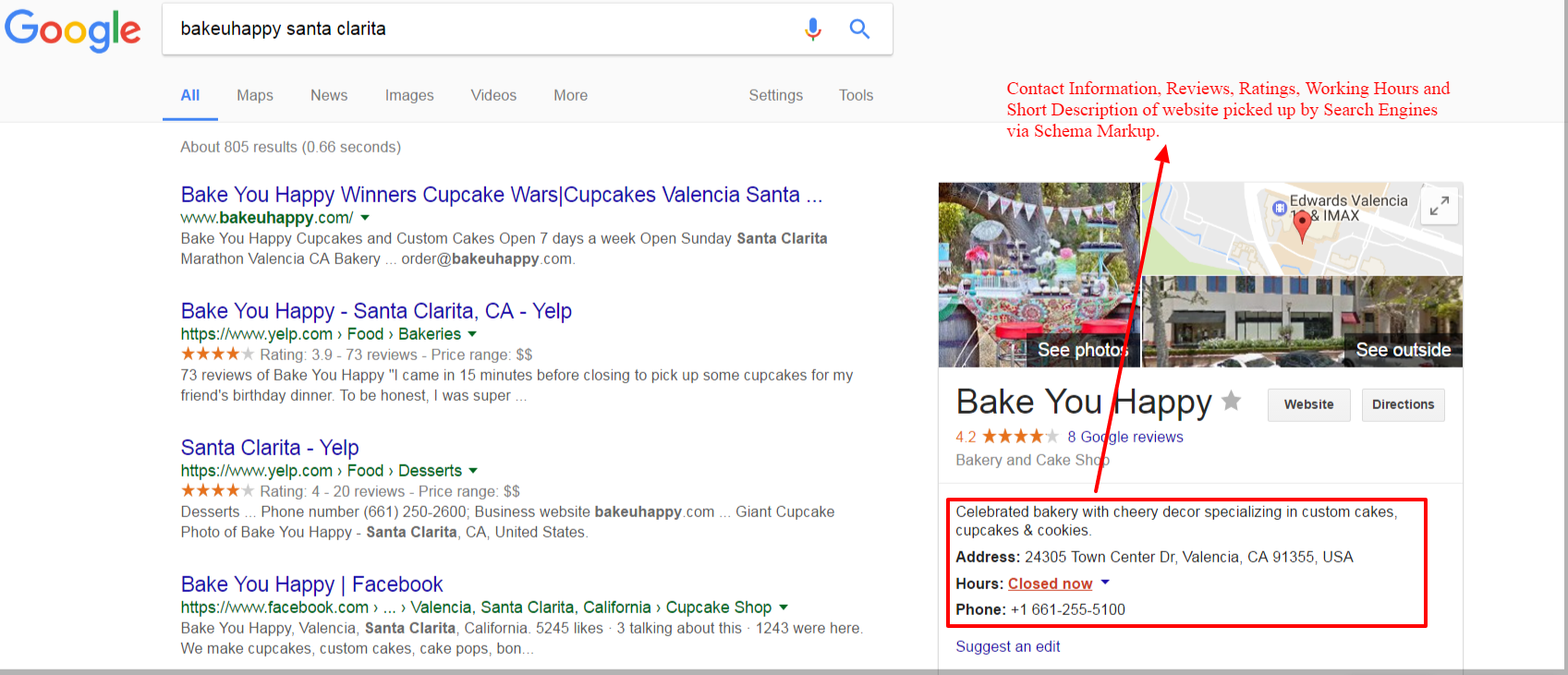
SEO’S have changed the digital marketing strategies ever since renowned search engines like YAHOO, Google, Bing, etc. changed their algorithms to favour a much more AI perspective.
Google’s announcement of the use of Rank Brain, as their artificial intelligence system aids in finding pages that don’t have the exact keywords mentioned in the search query.
In short, multiple factors now determine SERP, which makes the conventional ones such as keyword density, linking, and various other norms outdated.
CHANGE, get it? They did, so why can’t you?
Yet, not everyone stays updated and some prefer relying on age-old SEO tactics that were once or sometimes never a success. Hence, they falter from what was once a successful venture during one time, to an abysmal debacle.
The reputed British Broadcast Corporation, BBC was slapped with a penalty in the year 2013 for having unnatural links pointing towards a particular webpage.
In February 2011, Forbes.com was caught in the act of selling links on its own website, without a second thought of adding ‘no follow’ attribute.
You certainly don’t want that, do you?
Wrong SEO strategies prove to be a bane than a boon, and rightly so, they need to be avoided at all costs.
So which ones are outdated; how do you know which ones to stay away from and if there’s a diamond in the haystack, should you embrace them? Will it actually helpful?
1. Plagiarism:
There’s this huge misnomer in everyone’s mind that replicating the traits of successful companies or anything for that matter, guarantees success.
Nope.
While it’s good to owe inspiration from either the structure of the page or even the contextual combinations, blatant plagiarism is a huge demeanour.
No one wants to see the same thing twice.
Visitors who notice them jump to the conclusion that the webpage (propagating it to the business itself) isn’t inventive enough, and lacks knowledge, and prone to neglect.
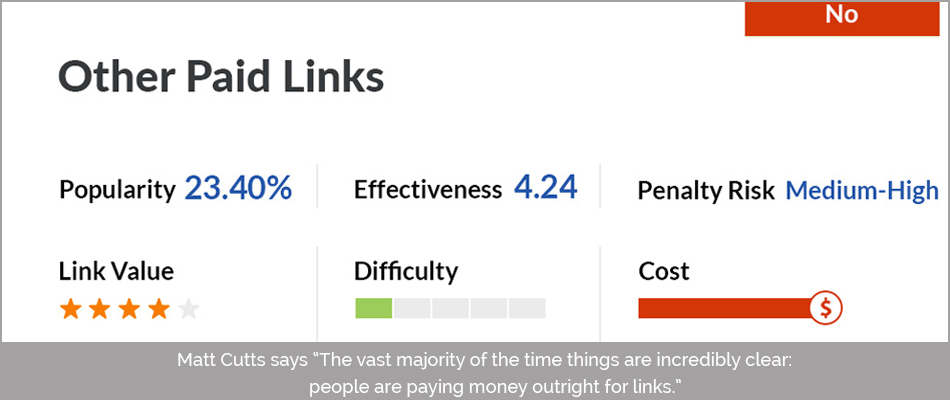
2. 3rd party “Paid” Links
What are you actually paying for?
Matt Cutts says “The vast majority of the time things are incredibly clear: people are paying money outright for links.”
Not only is it like taking the easiest route, these links may possess a stagnant structure that may have been replicated countless times.
Google and various other search engines have always been on the lookout for such stagnancy and they remove quite a few of them too.
Google banned Google Japan from buying paid links.
Now isn’t that enough to stop you?
3. Keyword Stuffing :
It’s one of the oldest tricks in the box still underuse. Not for anything good, at least.
So obviously, for your content to be recognized by the search engine the keywords need to stand out. Everyone knows that.
But stuffing a hundred keywords or so into it?
Not only is it unnatural, but it also hinders a certain level of user-friendliness, making it a viable technique to actually lose customers than anything more. Search Engines don’t like it either and you even stand the chance of being penalized and possibly banned.
It might’ve worked in the past when things were very simple but now, both the search engine algorithm and the visitor’s mindset are different.
How different?
Enough to not fall prey to gimmickry.
4. Bots, Spam, Ads, and ClickBaits :
A deadly dozen, to say the least.
Gone were the days when all the content on the web were tailor-made to the needs of the business or the website, and a writer painstakingly sits and writes each and every portion of the text.
With automation and artificial bots come not only the luxuries of having loads of contents prepared by the minute, but also a multitude of problems associated with it.
Why? Even they go crazy sometimes.
If a certain word repeats all over the content or maybe a similar structure elsewhere was already there, something could smell fishy.
Even if people may miss that, Search Engines do not and it may incur penalties or even less traffic than expected.
Clickbaits take use of flashy yet misleading headlines that would seem to be inviting to the visitor’s eye, particularly to gain traffic through visiting the links and even unknowingly sharing them.
There’s nothing much to say about ads and spam either. Who loves them? Want to make extra money? Improve the content and not resort to stuff like these.
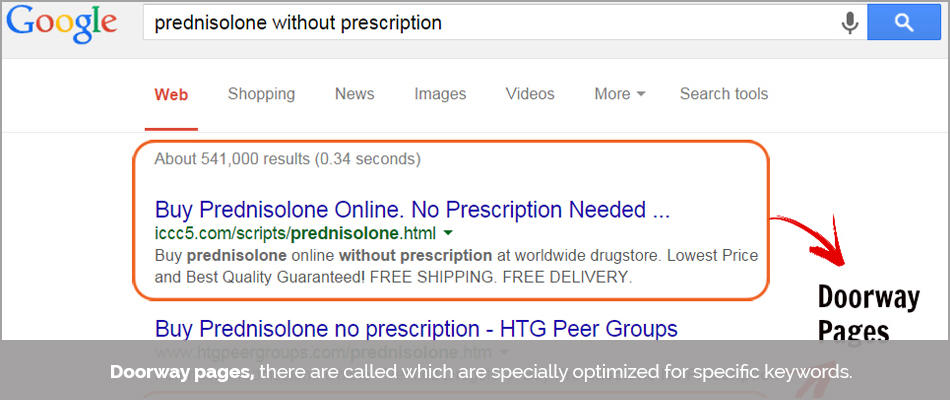
5. Cloaking:
Cloaking is merely “sophisticated hiding”.
It’s like presenting a rigged version of the actual webpage such that it satisfies the algorithm of the search engine and hence can be called upon when the visitor searches for the particular keyword.
Doorway pages, there are called which are specially optimized for specific keywords. The page altogether may be entirely different, and may even serve another purpose probably with even questionable content.
Google has banned Cloaking of any form, need I say more?
British Motor Works (BMW) was penalized for cloaking in 2006.
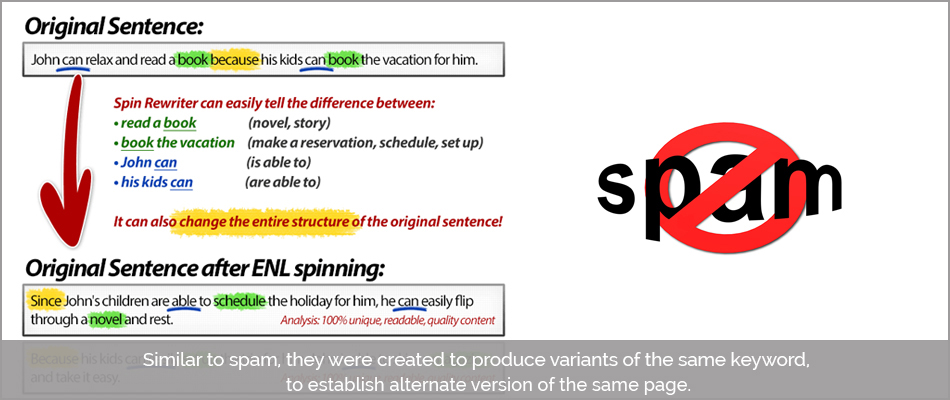
6. Article Spinners :
Similar to spam, they were created to produce variants of the same keyword, to establish an alternate version of the same page.
This in turn gave rise to numerous low-quality articles and Search Engine algorithms like Google Hummingbird got updated to further filter out unnecessary variants.
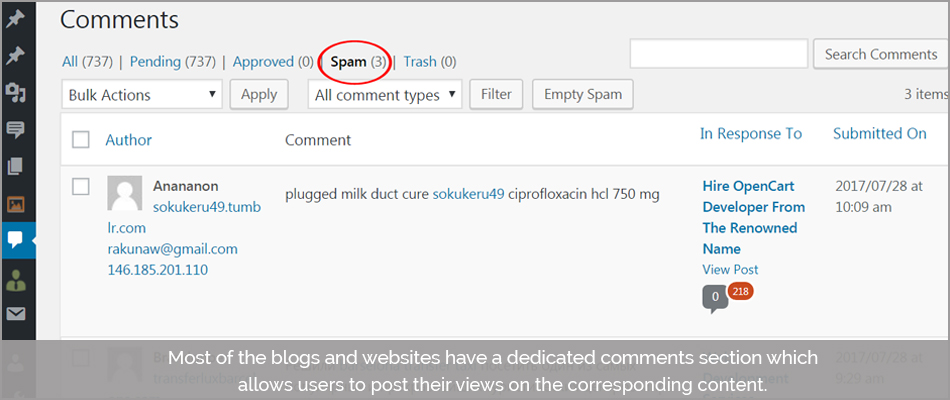
7. Spam Comments
Most of the blogs and websites have a dedicated comments section that allows users to post their views on the corresponding content.
However, this was prone to misuse since a lot of bloggers put website links as well, along with the comments – a genuinely false move to induce traffic.
More or less- SPAM.
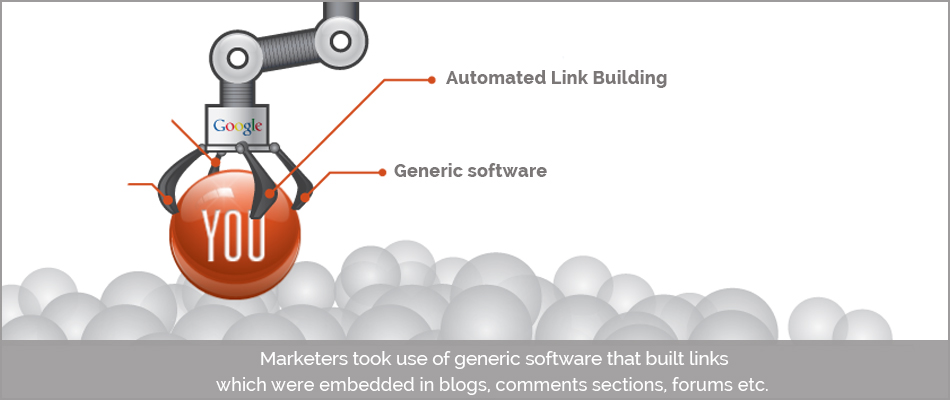
8. Automated Link Building:
Marketers took use of generic software that built links that were embedded in blogs, comments sections, forums etc. They would mostly be redirected to numerous articles that were generally very poorly written.
An ultimate time waster, especially since they might seem to contain information we think we might actually need but often end up as a huge disappointment.
Rap Genius, the famous lyrics-based site fell prey to Automated link building; they faced consequences from Google for allowing users to post links alongside lyrics content resulting in an unnatural hike in traffic.
9. Interlinking Websites :
The wrong thing here would be striking the perfect balance between what’s useful and what’s abuse.
Many websites require interlinking them with others for a steady flow of information and even to redirect the user according to their wish.
The problem lies in its misuse. In most cases, arrays of unwanted websites are interlinked of which none might be relevant.
The Google AI has the skill to notice patterns within interlinking spam for its use and it efficiently curbs the rise in low content irrelevant links.
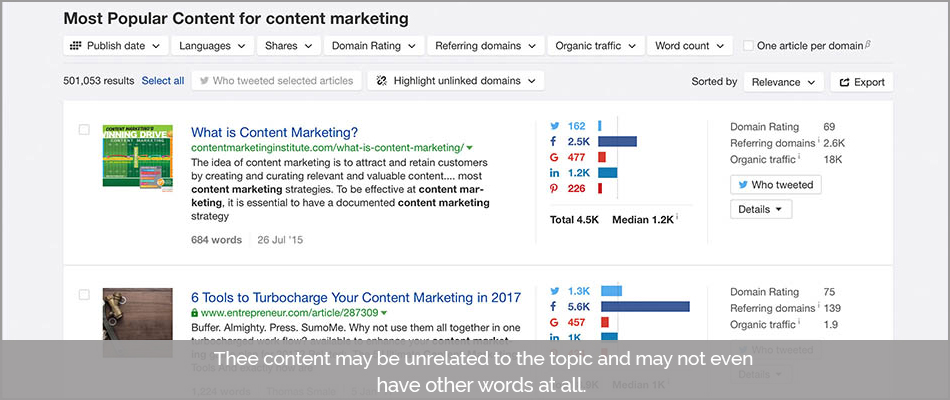
10. Short /Thin form Content:
Most of the websites used to get away with this technique where a short word pertaining to nothing specific other than the use of the same word 2-3 times would allow search traffic for their site.
The content may be unrelated to the topic and may not even have other words at all.
11. Link and Article Directories :
The Panda Update for Google’s AI bought to a close, the misuse of these directories which basically allowed websites to be categorized based on the needs of the user.
However, misuse crept in especially due to the simplicity of installing the software which powers them, allowing them to create multiple irrelevant links.
Article Directories were even worse. They were rewritten and became bloated with low-quality content.
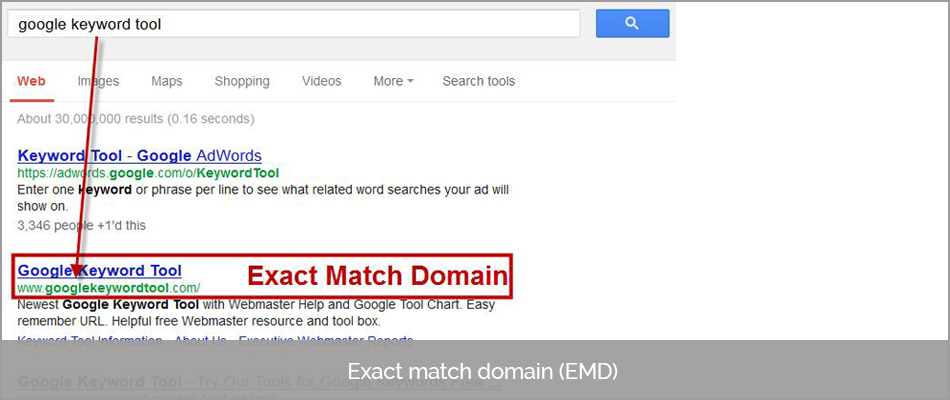
12. Exact Match Domains :
Matching the domain with the exact keyword phrase allowed microsites such as these to rank up higher than the actual domain for multiple days.
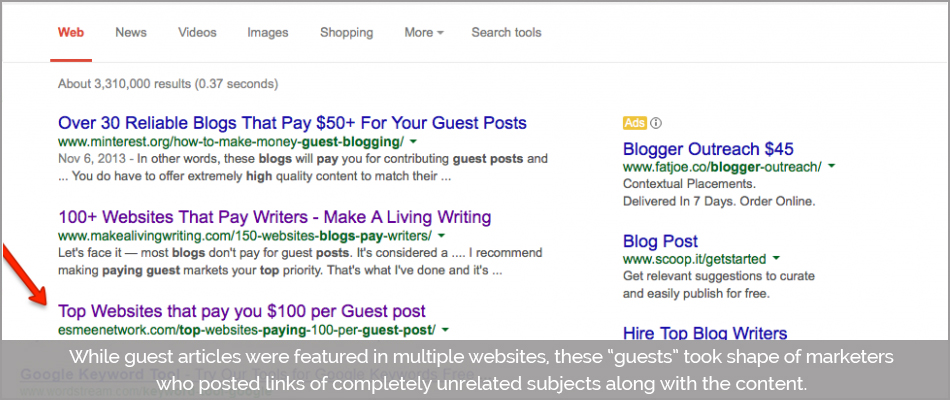
13. Paid/ Spammy Guest Blogging
This went out of hand mainly due to its uncontrollable nature.
While guest articles were featured on multiple websites, these “guests” took shape of marketers who posted links of completely unrelated subjects along with the content.
A wide flurry of such tactics furthered the need to retrospectively control the content before posting it on the website, and with AI alterations they were taken to their traditional grassroots, favoring the actual content developers.
14. Online Press Releases :
Wannabe website services mimic real journalists by shooting out online press releases with the desire to be scraped up by other websites to induce traffic for their own venture.
Not only is it a genuine time waster, but these releases would also be sold out by sub-standard websites with less visibility that doesn’t offer anything to the client sites which buy them as well.